Kid Dictionary Genetic Engineering

Information and translations of genetic engineering in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web.
Kid dictionary genetic engineering. They make up the material called dna which is found in the cells of every living thing. Genetic engineering sometimes called genetic modification is the process of altering the dna in an organism s genome. What does genetic engineering mean.
Genetic engineering is the process of manipulating or changing a living thing s dna in order to make the living thing have certain characteristics. It may also mean extracting dna from another organism s genome and combining it with the dna of that individual. Search the meaning and definition of over one hundred thousand words.
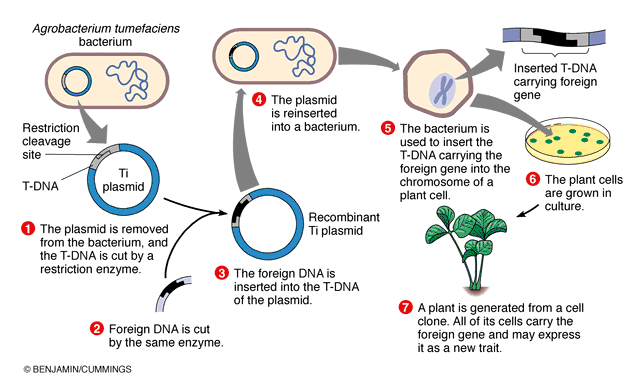
By the mid 1970s scientists had learned how to locate remove and insert specific genes in dna. Genetic engineering definition is the group of applied techniques of genetics and biotechnology used to cut up and join together genetic material and especially dna from one or more species of organism and to introduce the result into an organism in order to change one or more of its characteristics. Genetic engineering genetic modification gm and gene splicing once in widespread use but now depricated describe the process of manipulating genes in an animal or plant outside of the organism s normal reproductive process.
By the 1990s scientists could clone animals or produce animals that have exactly the same dna as another animal. Genetic engineering definition the development and application of scientific methods procedures and technologies that permit direct manipulation of genetic material in order to alter the hereditary traits of a cell organism or population. What is genetic engineering.
This work is called genetic engineering. Meaning of genetic engineering. Genes are tiny units that carry information about an organism.
How to use genetic engineering in a sentence. Genetic engineering dates to 1973 when two american scientists cut and rejoined bits of dna. In 1996 researchers in scotland produced the first clone of an adult mammal a sheep.